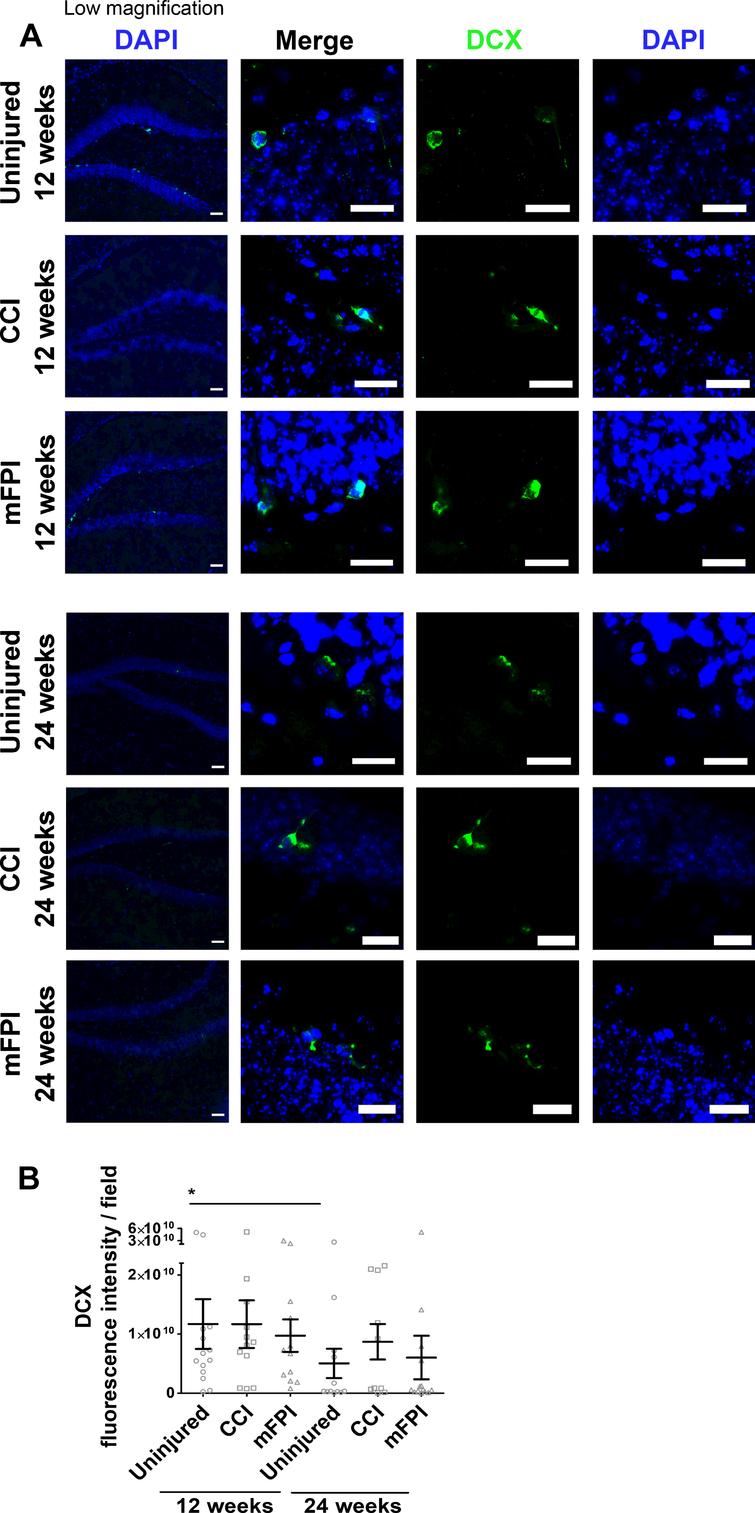
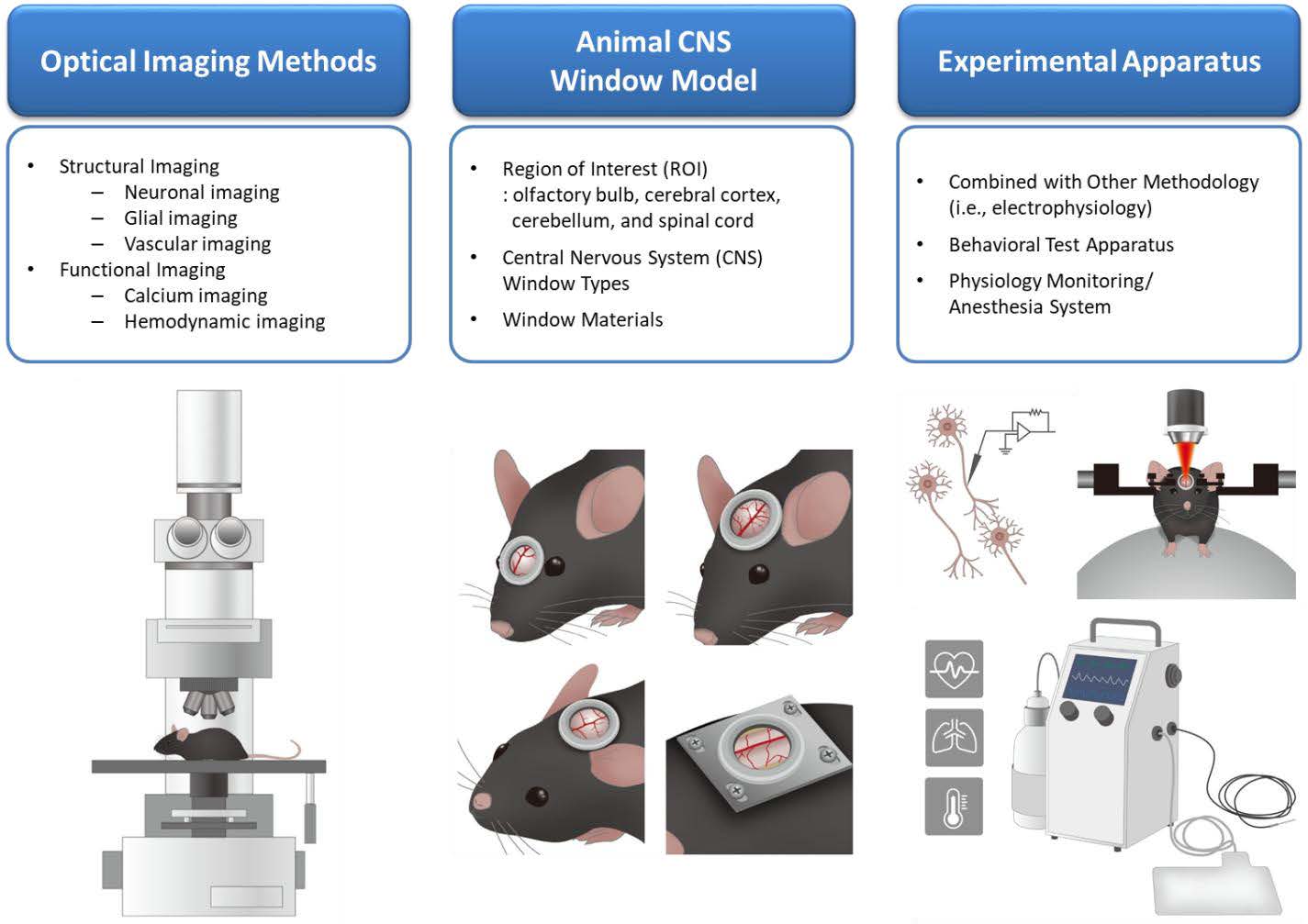
Angiopoietin/Tie2 Axis Regulates the Age-at-Injury Cerebrovascular Response to Traumatic Brain Injury | Journal of Neuroscience

Case studies in neuroscience: reversible signatures of edema following electric and piezoelectric craniotomy drilling in macaques | Journal of Neurophysiology
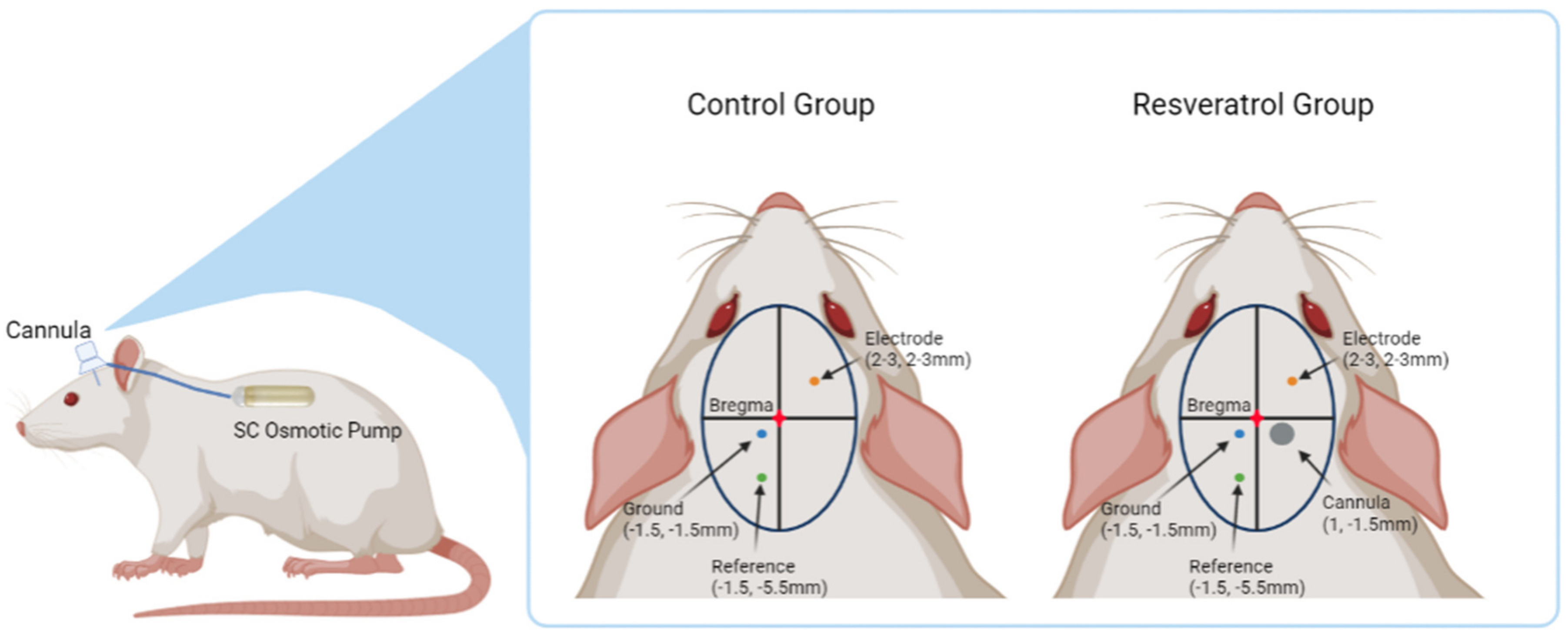
Micromachines | Free Full-Text | Investigation of the Feasibility of Ventricular Delivery of Resveratrol to the Microelectrode Tissue Interface | HTML

Synchrotron Radiation-Based FTIR Microspectroscopic Imaging of Traumatically Injured Mouse Brain Tissue Slices | ACS Omega
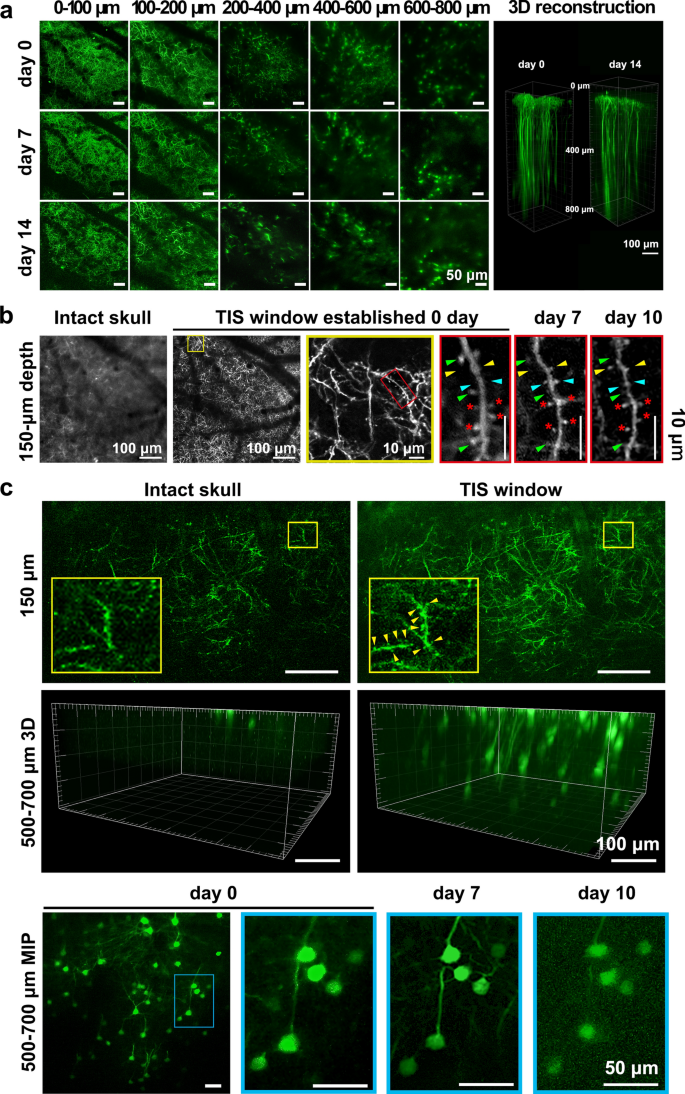
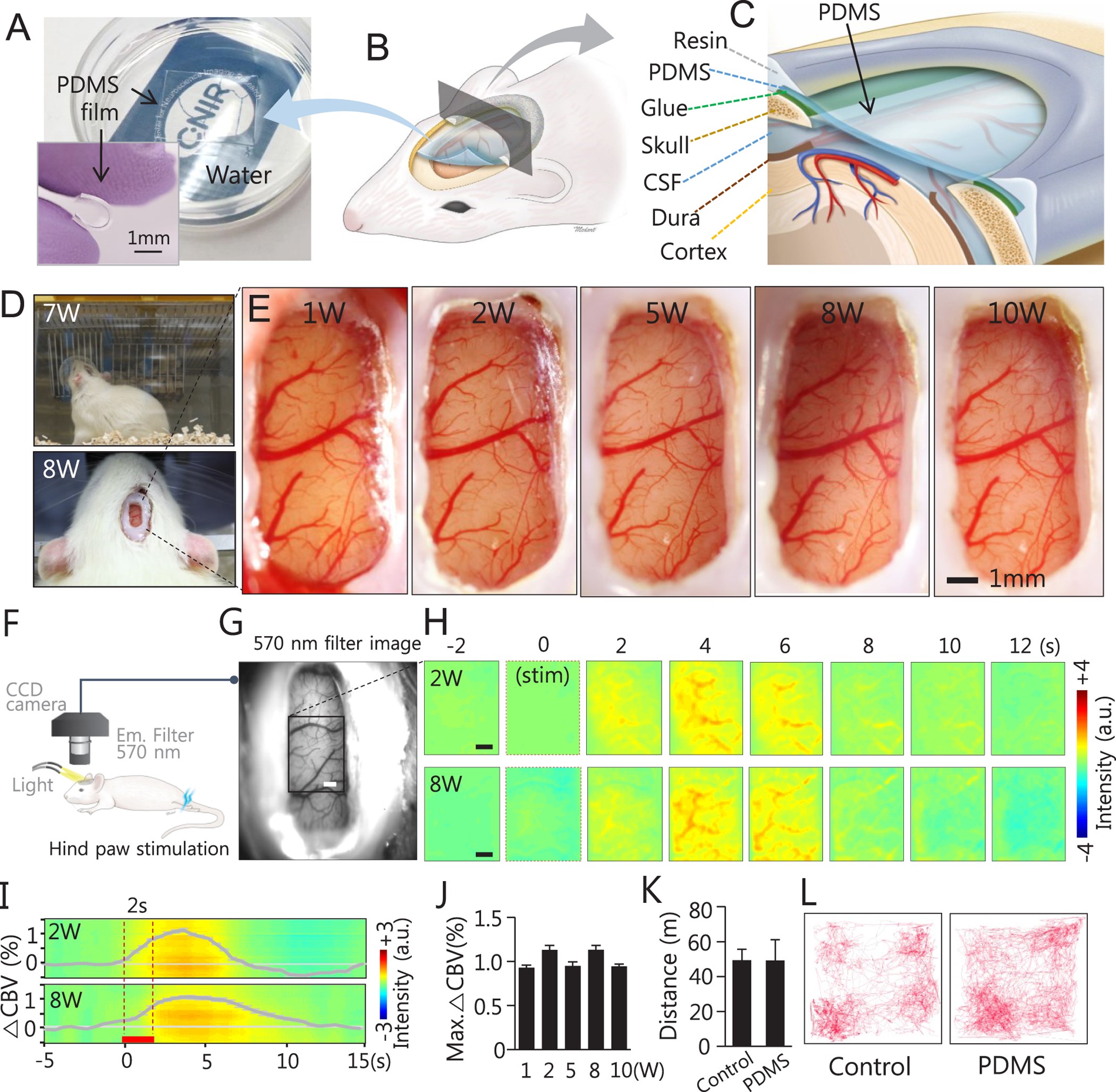
A Through-Intact-Skull (TIS) chronic window technique for cortical structure and function observation in mice | eLight | Full Text

Blood–Brain Barrier Disruption in Preclinical Mouse Models of Stroke Can Be an Experimental Artifact Caused by Craniectomy | eNeuro

STAT1 Contributes to Microglial/Macrophage Inflammation and Neurological Dysfunction in a Mouse Model of Traumatic Brain Injury | Journal of Neuroscience

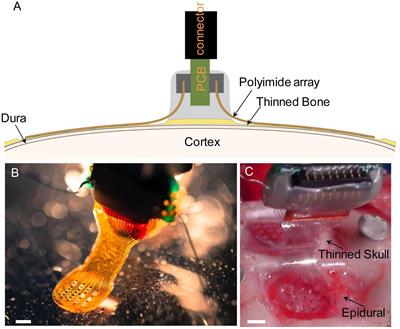
Early posttraumatic CSF1R inhibition via PLX3397 leads to time- and sex-dependent effects on inflammation and neuronal maintenance after traumatic brain injury in mice - ScienceDirect
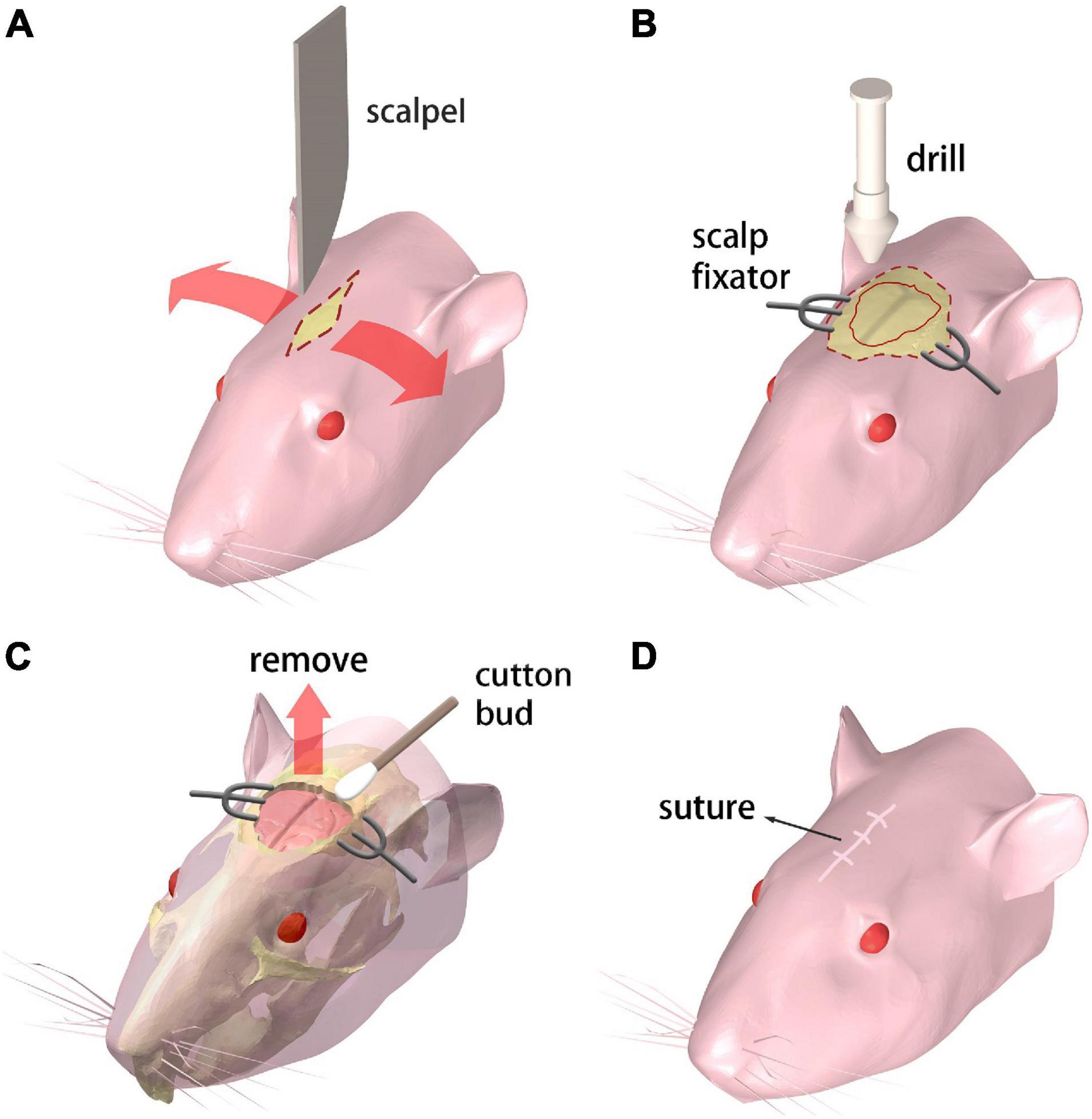
Frontiers | A Skull-Removed Chronic Cranial Window for Ultrasound and Photoacoustic Imaging of the Rodent Brain

Measurement of cerebral oxygen pressure in living mice by two-photon phosphorescence lifetime microscopy: STAR Protocols

Engineered glycomaterial implants orchestrate large-scale functional repair of brain tissue chronically after severe traumatic brain injury | Science Advances
Rapamycin Attenuates the Development of Posttraumatic Epilepsy in a Mouse Model of Traumatic Brain Injury | PLOS ONE
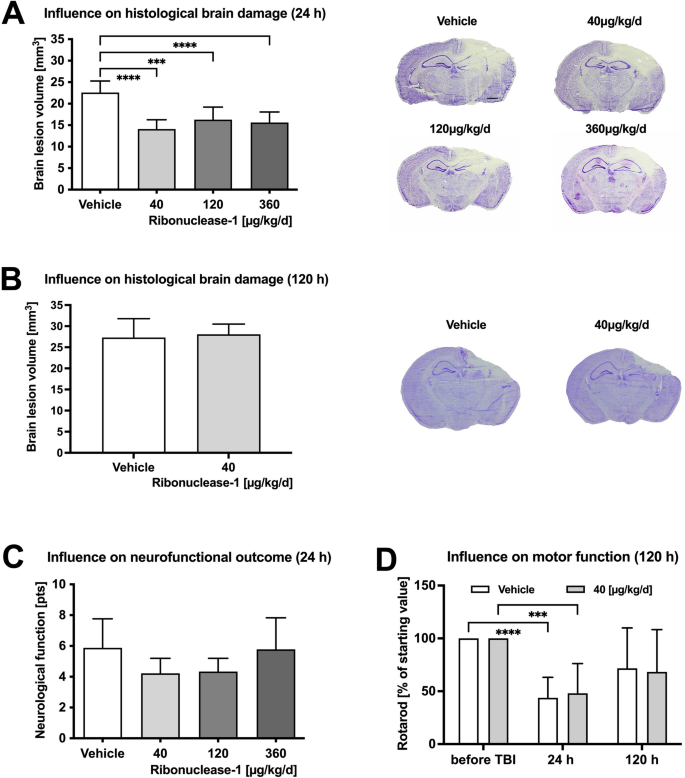
Ribonuclease-1 treatment after traumatic brain injury preserves blood–brain barrier integrity and delays secondary brain damage in mice | Scientific Reports

Microvascular Injury in Mild Traumatic Brain Injury Accelerates Alzheimer-like Pathogenesis in Mice | bioRxiv

Measurement of cerebral oxygen pressure in living mice by two-photon phosphorescence lifetime microscopy: STAR Protocols

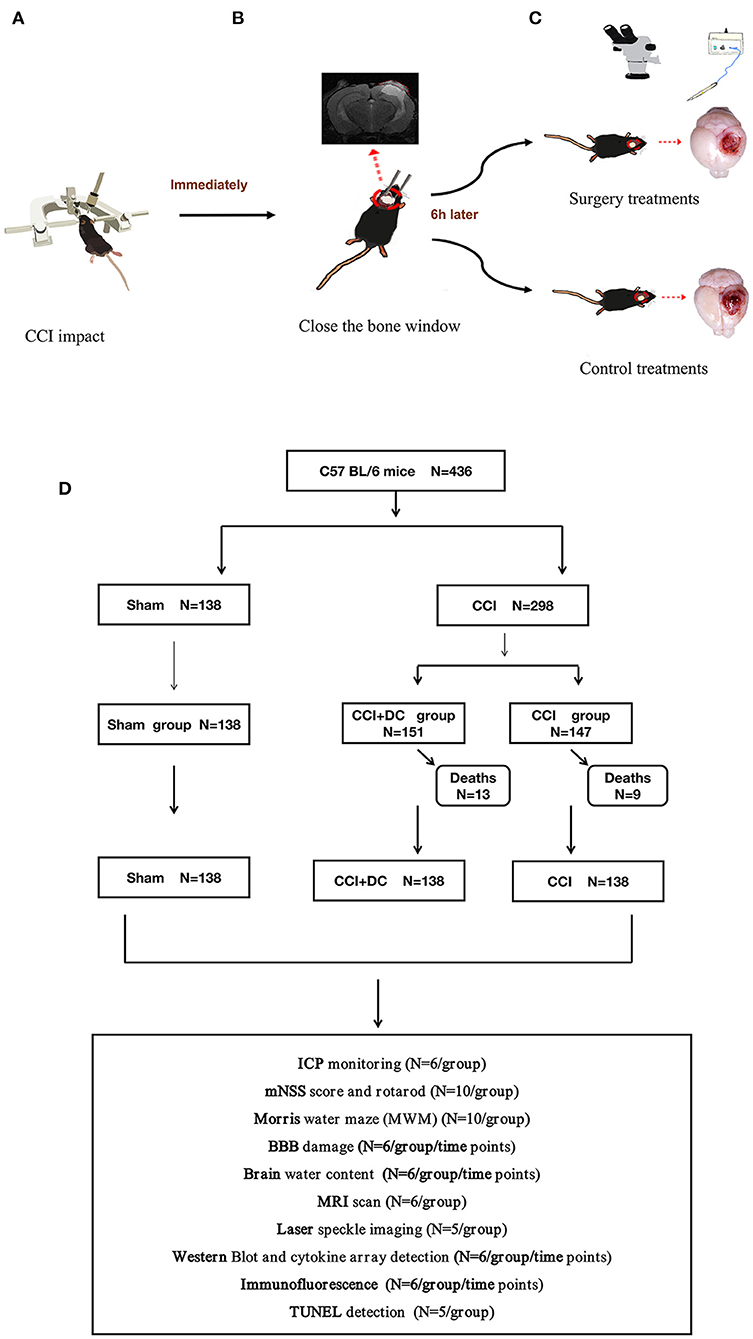
Establishment and Evaluation of a Novel High-Efficiency Model of Graded Traumatic Brain Injury in Mice - ScienceDirect
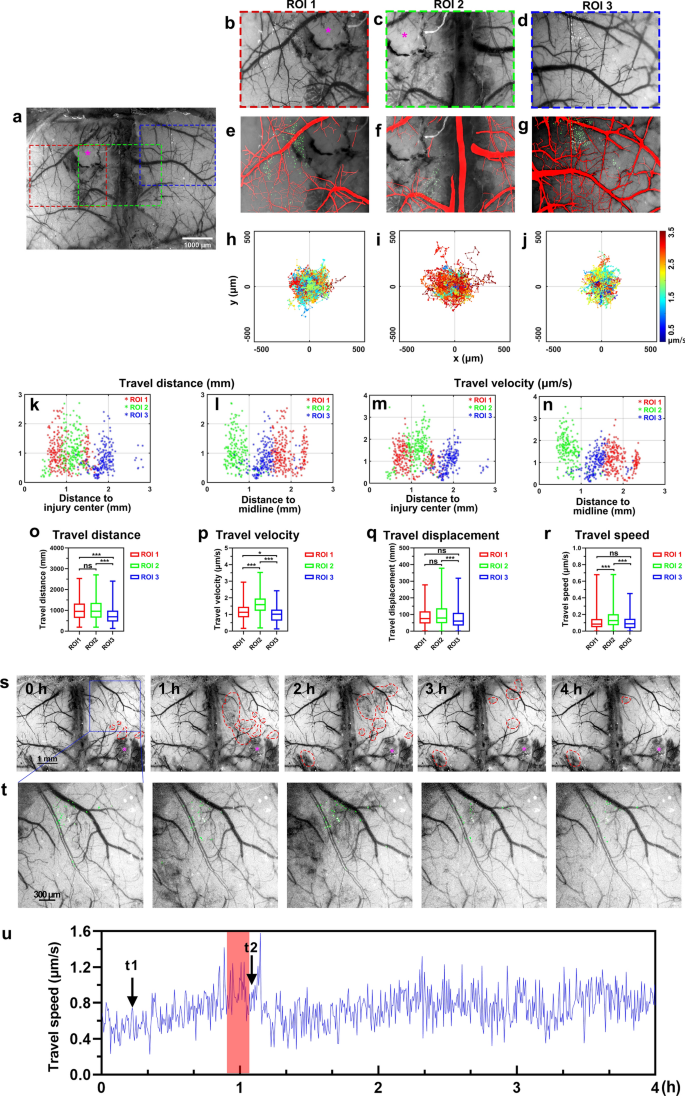
A Through-Intact-Skull (TIS) chronic window technique for cortical structure and function observation in mice | eLight | Full Text